No bet left behind.
No bet left behind.
No bet left behind.
Bet matching on Wagr.
Bet matching on Wagr.
Bet matching on Wagr.



Context
Context
Wagr is a startup that sought to combine sports betting with consumer social. It was a platform where friends could bet against one another on their favorite games in a way that was friendly, safe, and fun.
Bet matching was a feature that sought to combat high churn rates by expanding the network of who could receive bets on the platform.
As the designer for this project, I spearheaded the user research, detailed user flows, and crafted hi-fi prototypes.
Wagr is a startup that sought to combine sports betting with consumer social. It was a platform where friends could bet against one another on their favorite games in a way that was friendly, safe, and fun.
Bet matching was a feature that sought to combat high churn rates by expanding the network of who could receive bets on the platform.
As the designer for this project, I spearheaded the user research, detailed user flows, and crafted hi-fi prototypes.
Role
Role
Product Design, Prototyping
Product Design, Prototyping
Tools
Tools
Figma, Origami Studio
Figma, Origami Studio
Timeline
Timeline
April 2022 - August 2022
April 2022 - August 2022



How to not leave behind bets.
How to not leave behind bets.
How to not leave behind bets.
A how-to guide you can trust.
A how-to guide you can trust.
A how-to guide you can trust.
Step 0: Context
Step 0: Context
Step 0: Context
What differs Wagr from other sports betting platforms?
What differs Wagr from other sports betting platforms?
What differs Wagr from other sports betting platforms?
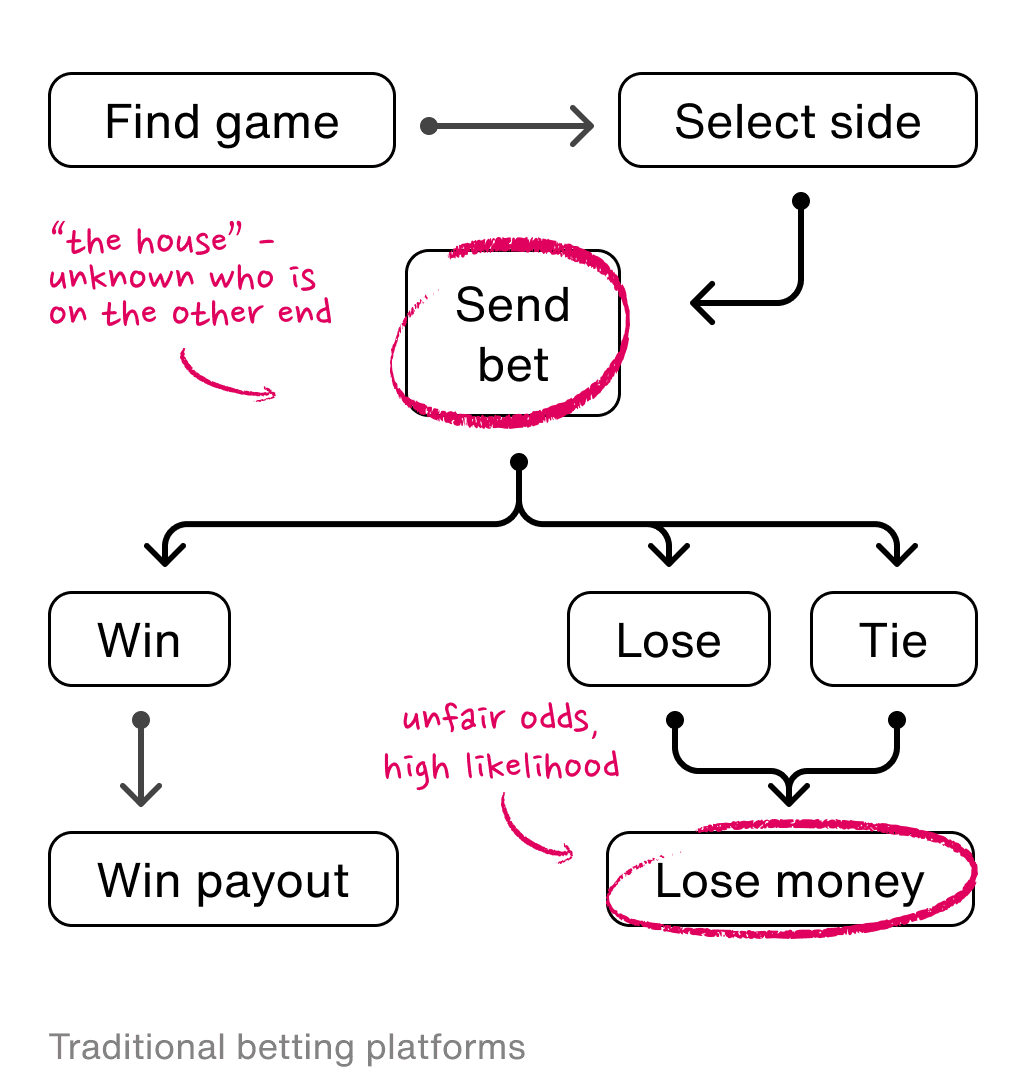
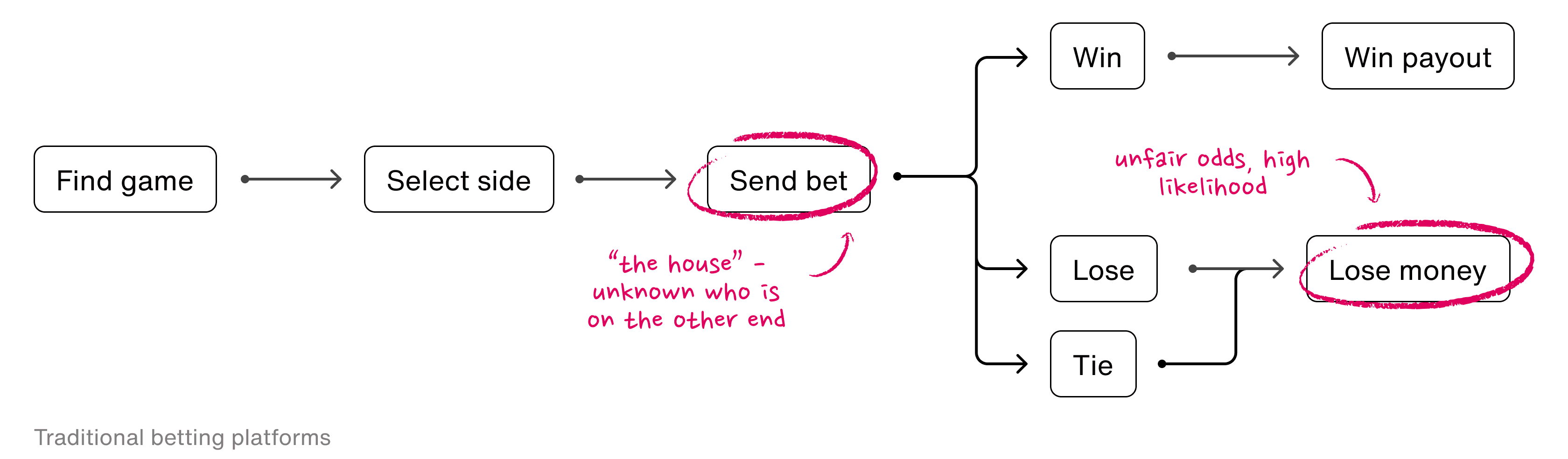
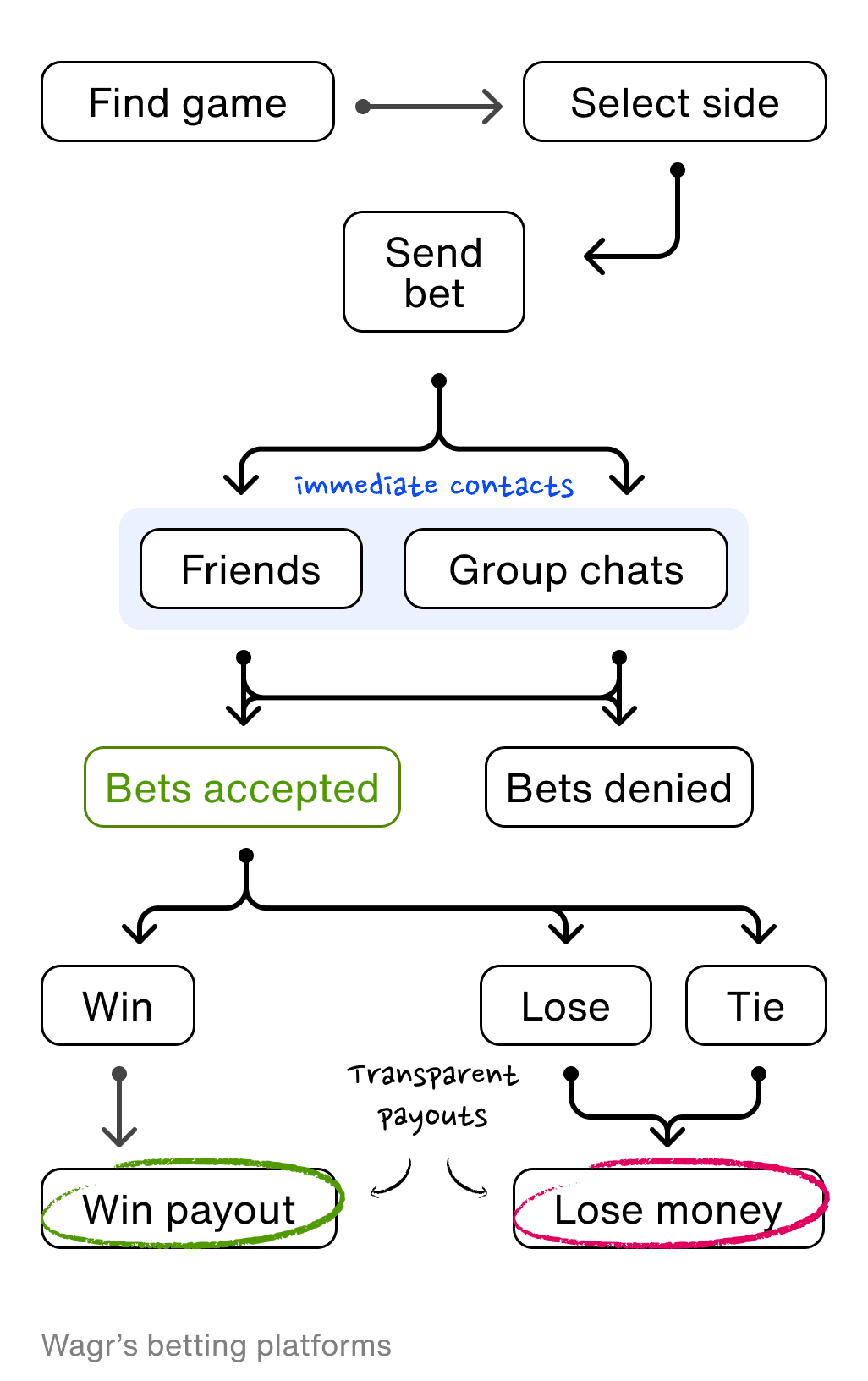
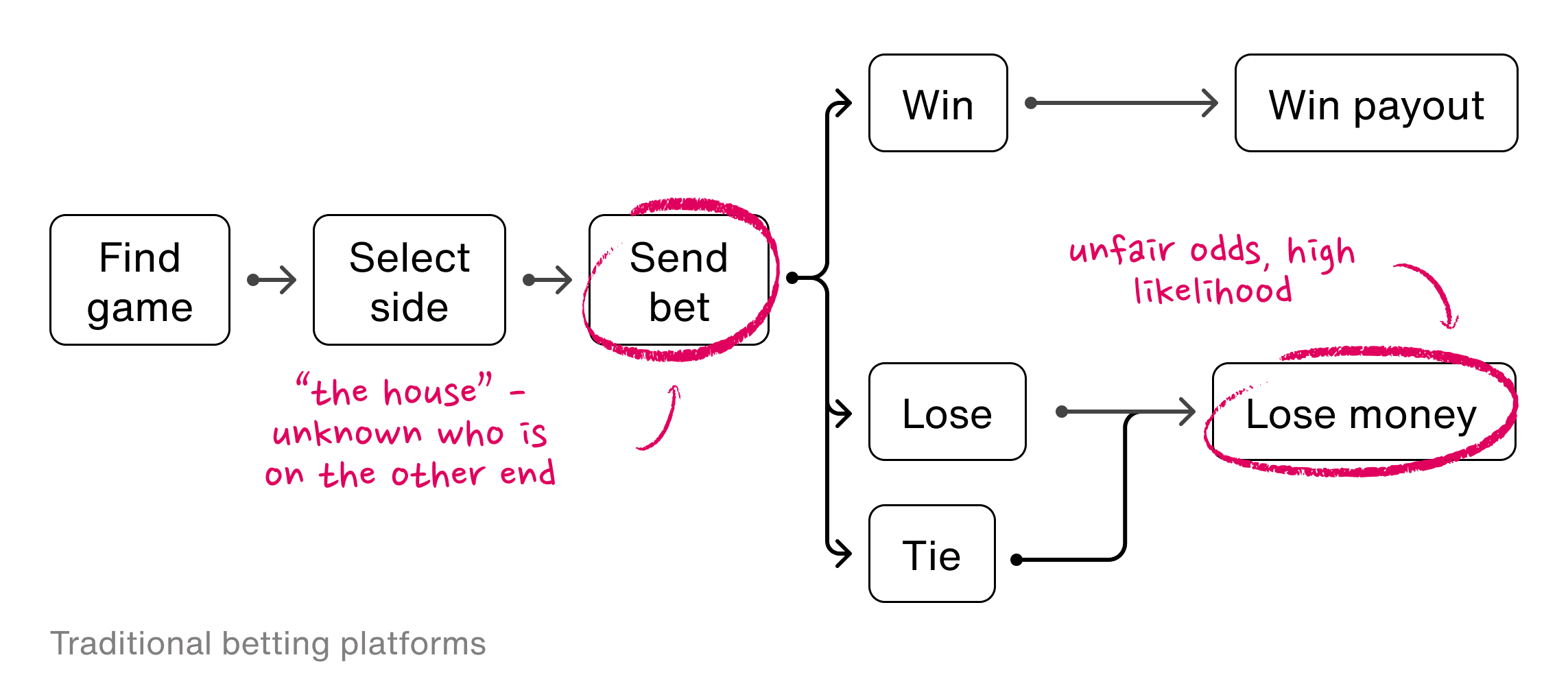
Wagr allows users to know who is on the other side of their bets by shifting the focus from betting against the "house" to betting against people in a user's social network
Wagr allows users to know who is on the other side of their bets by shifting the focus from betting against the "house" to betting against people in a user's social network
Wagr allows users to know who is on the other side of their bets by shifting the focus from betting against the "house" to betting against people in a user's social network


Step 1: Identify the problem
Step 1: Identify the problem
Step 1: Identify the problem
The first step to changing is to be honest with yourself and the situation that you are in. Here is when I did that.
The first step to changing is to be honest with yourself and the situation that you are in. Here is when I did that.
The first step to changing is to be honest with yourself and the situation that you are in. Here is when I did that.
Wagr was witnessing high churn rates right after users invited their friends to take on the other side
Wagr was witnessing high churn rates right after users invited their friends to take on the other side
Wagr was witnessing high churn rates right after users invited their friends to take on the other side
Users would determine who took their bets through direct invites. However, most bets were ignored or unaccepted. When users experienced their bets not going through their full lifecycle, they were more likely to leave the platform.
Users would determine who took their bets through direct invites. However, most bets were ignored or unaccepted. When users experienced their bets not going through their full lifecycle, they were more likely to leave the platform.
Users would determine who took their bets through direct invites. However, most bets were ignored or unaccepted. When users experienced their bets not going through their full lifecycle, they were more likely to leave the platform.



Step 2: Research, reflect, rework
Step 2: Research, reflect, rework
Step 2: Research, reflect, rework
I conducted user research and tested a couple hypothesis as to why bets were not being taken.
I conducted user research and tested a couple hypothesis as to why bets were not being taken.
I conducted user research and tested a couple hypothesis as to why bets were not being taken.
Why were users turning down bets?
Why were users turning down bets?
Why were users turning down bets?
I had initially designed Wagr so that users would invite their friends to take on the opposing side of the bet. However, I realized that most users in the same friend groups enjoy the same sports teams and are unlikely to bet on their rivals.
I had initially designed Wagr so that users would invite their friends to take on the opposing side of the bet. However, I realized that most users in the same friend groups enjoy the same sports teams and are unlikely to bet on their rivals.
I had initially designed Wagr so that users would invite their friends to take on the opposing side of the bet. However, I realized that most users in the same friend groups enjoy the same sports teams and are unlikely to bet on their rivals.
Wrong side?
Wrong side?
Wrong side?
Were users expected to support teams they didn't love in real life?
Were users expected to support teams they didn't love in real life?
Were users expected to support teams they didn't love in real life?
Verdict: Yes
Verdict: Yes
Verdict: Yes
Users were turning down bets for teams they didn't already support
Users were turning down bets for teams they didn't already support
Users were turning down bets for teams they didn't already support
Was the price not right?
Was the price not right?
Was the price not right?
Were users rejecting bets because they were too expensive?
Were users rejecting bets because they were too expensive?
Were users rejecting bets because they were too expensive?
Verdict: No
Verdict: No
Verdict: No
Users were accepting bets of all price ranges
Users were accepting bets of all price ranges
Users were accepting bets of all price ranges
Stranger danger?
Stranger danger?
Stranger danger?
Were users rejecting bets from people they didn't know?
Were users rejecting bets from people they didn't know?
Were users rejecting bets from people they didn't know?
Verdict: No
Verdict: No
Verdict: No
Bets were taken regardless of relationship
Bets were taken regardless of relationship
Bets were taken regardless of relationship



Mapping out the key issue
Mapping out the key issue
Mapping out the key issue
When users were only limited to sending bets to their immediate networks, there was a higher likelihood that bets were rejected. This was especially true if the individual sending and the individual receiving the bet were fans of the same teams.
When users were only limited to sending bets to their immediate networks, there was a higher likelihood that bets were rejected. This was especially true if the individual sending and the individual receiving the bet were fans of the same teams.
When users were only limited to sending bets to their immediate networks, there was a higher likelihood that bets were rejected. This was especially true if the individual sending and the individual receiving the bet were fans of the same teams.
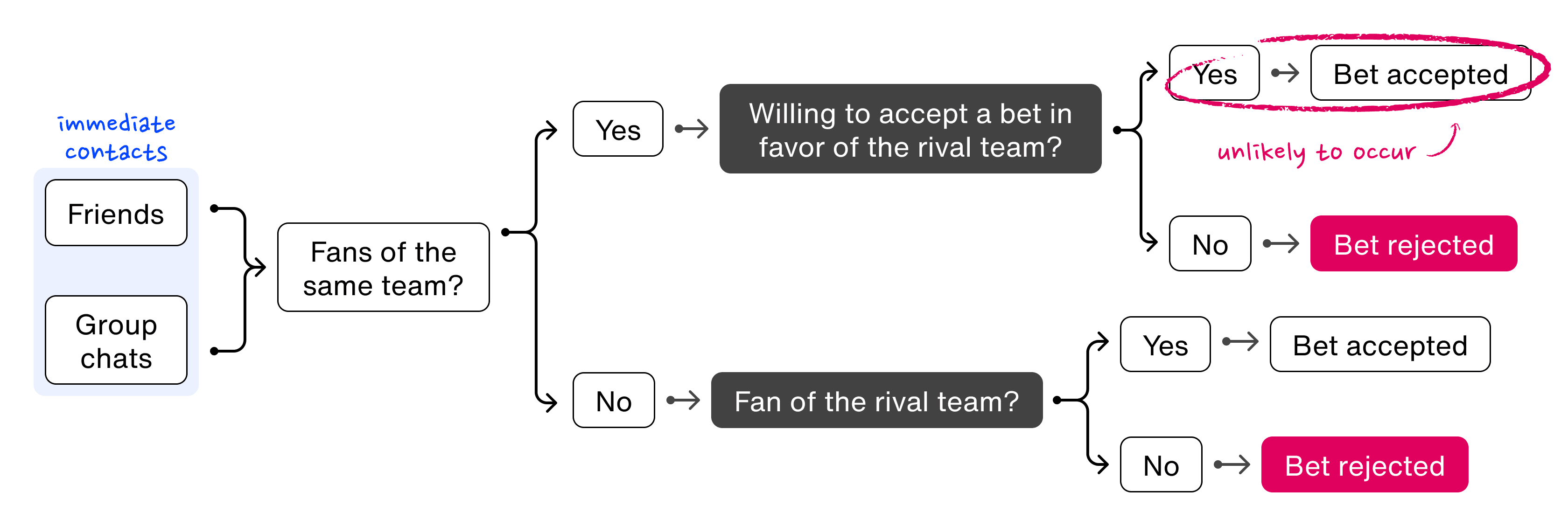
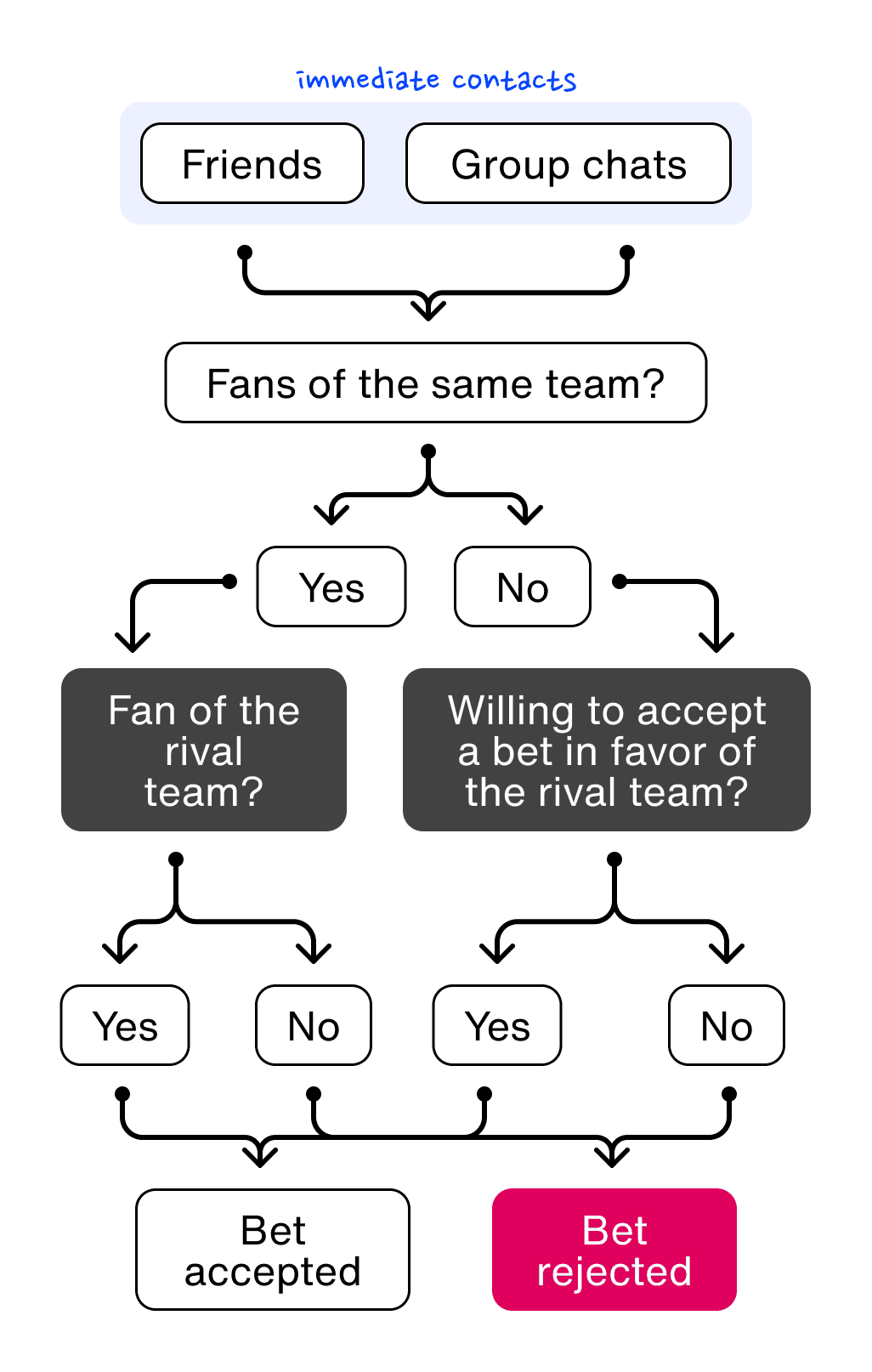
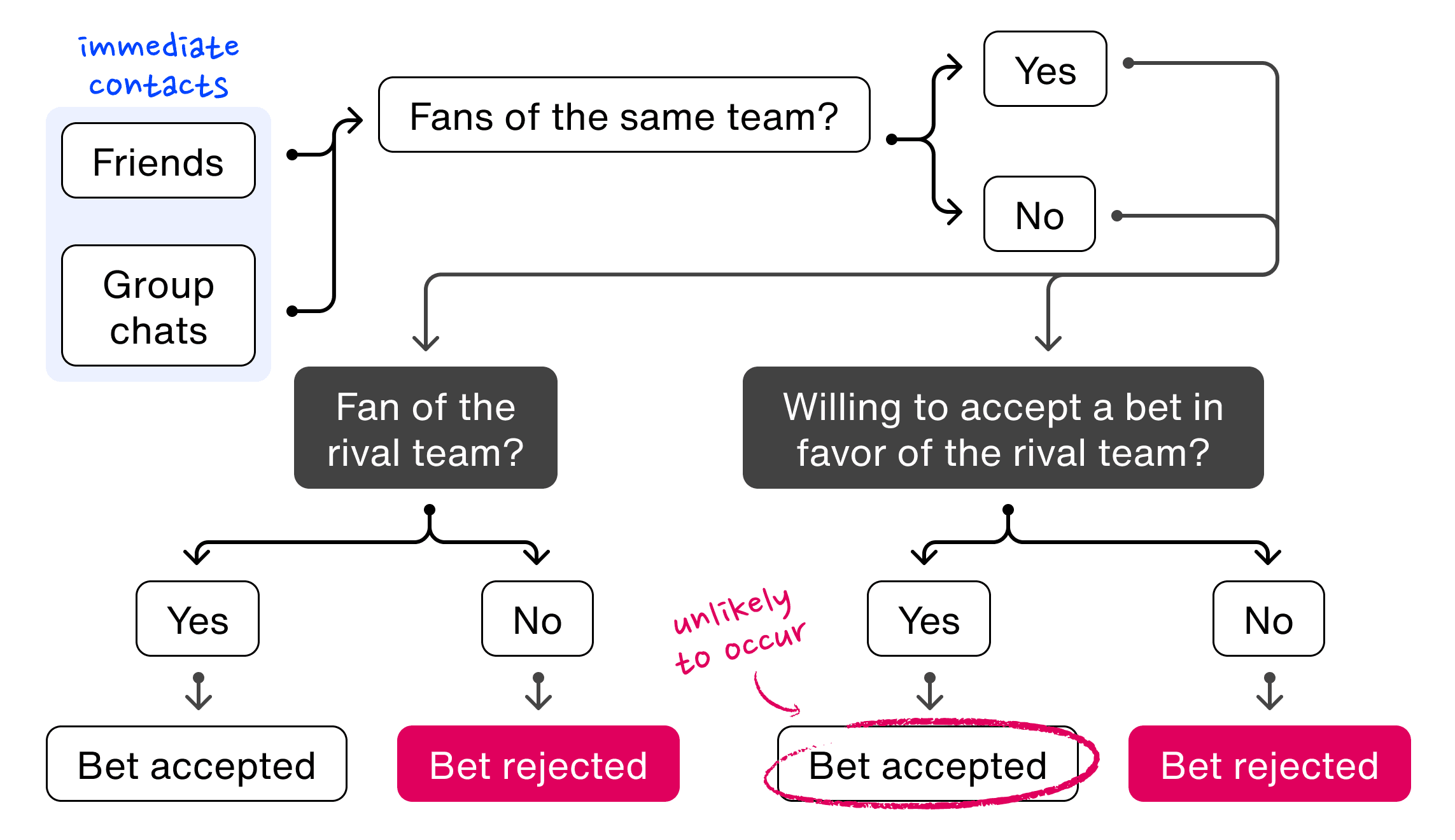
Identifying an opportunity from data
Identifying an opportunity from data
Identifying an opportunity from data
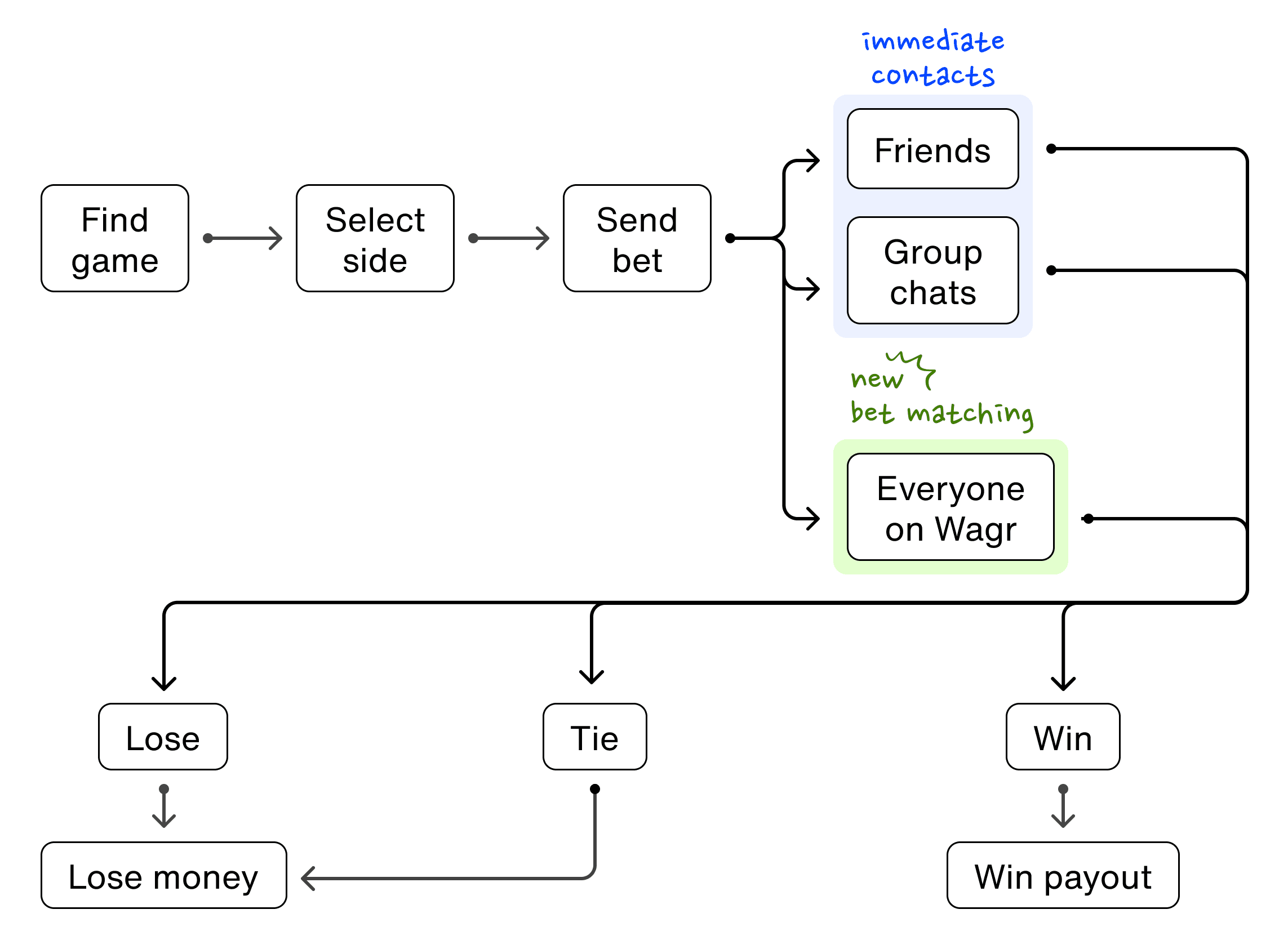
How might I create a new flow that allows users' bets to be matched with anyone on Wagr as opposed to just their immediate network?
How might I create a new flow that allows users' bets to be matched with anyone on Wagr as opposed to just their immediate network?
How might I create a new flow that allows users' bets to be matched with anyone on Wagr as opposed to just their immediate network?
At the core, users wanted to have their bets taken by someone on the other side. Based on the data, it did not matter significantly if the bet was taken on by someone who was not in a user's immediate network.
At the core, users wanted to have their bets taken by someone on the other side. Based on the data, it did not matter significantly if the bet was taken on by someone who was not in a user's immediate network.
At the core, users wanted to have their bets taken by someone on the other side. Based on the data, it did not matter significantly if the bet was taken on by someone who was not in a user's immediate network.
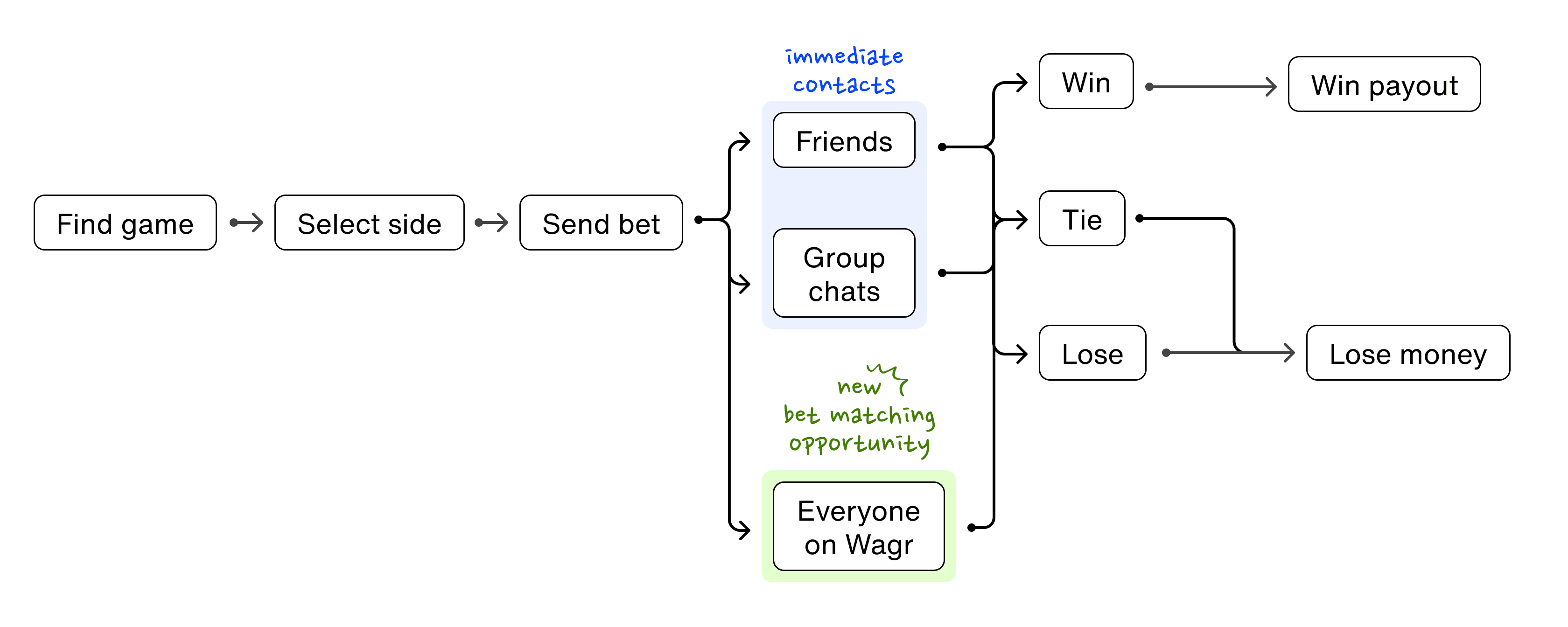

Step 3: Create a game plan
Step 3: Create a game plan
Step 3: Create a game plan
Identifying the key areas for feature implementation
Identifying the key areas for feature implementation
Identifying the key areas for feature implementation
What flows will be most impacted by the introduction of bet matching?
What flows will be most impacted by the introduction of bet matching?
What flows will be most impacted by the introduction of bet matching?
Where on Wagr would introducing bet matching be most effective?
Where on Wagr would introducing bet matching be most effective?
Where on Wagr would introducing bet matching be most effective?
Home screen
Home screen
Home screen
Bet confirmation
Bet confirmation
Bet confirmation
Invite friends
Invite friends
Invite friends
Step 4: Execute the game plan
Step 4: Execute the game plan
Step 4: Execute the game plan
Maximizing our odds of success
Maximizing our odds of success
Maximizing our odds of success
What bets are being matched?
What bets are being matched?
What bets are being matched?
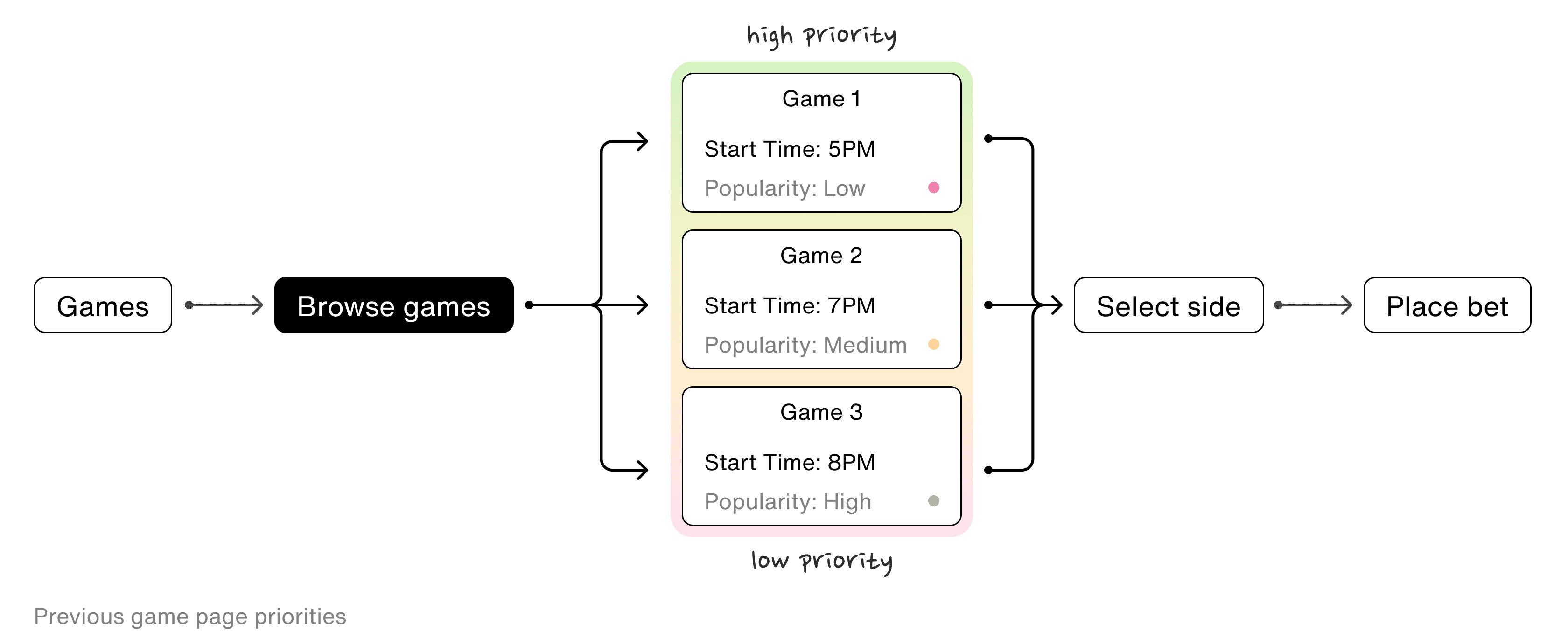
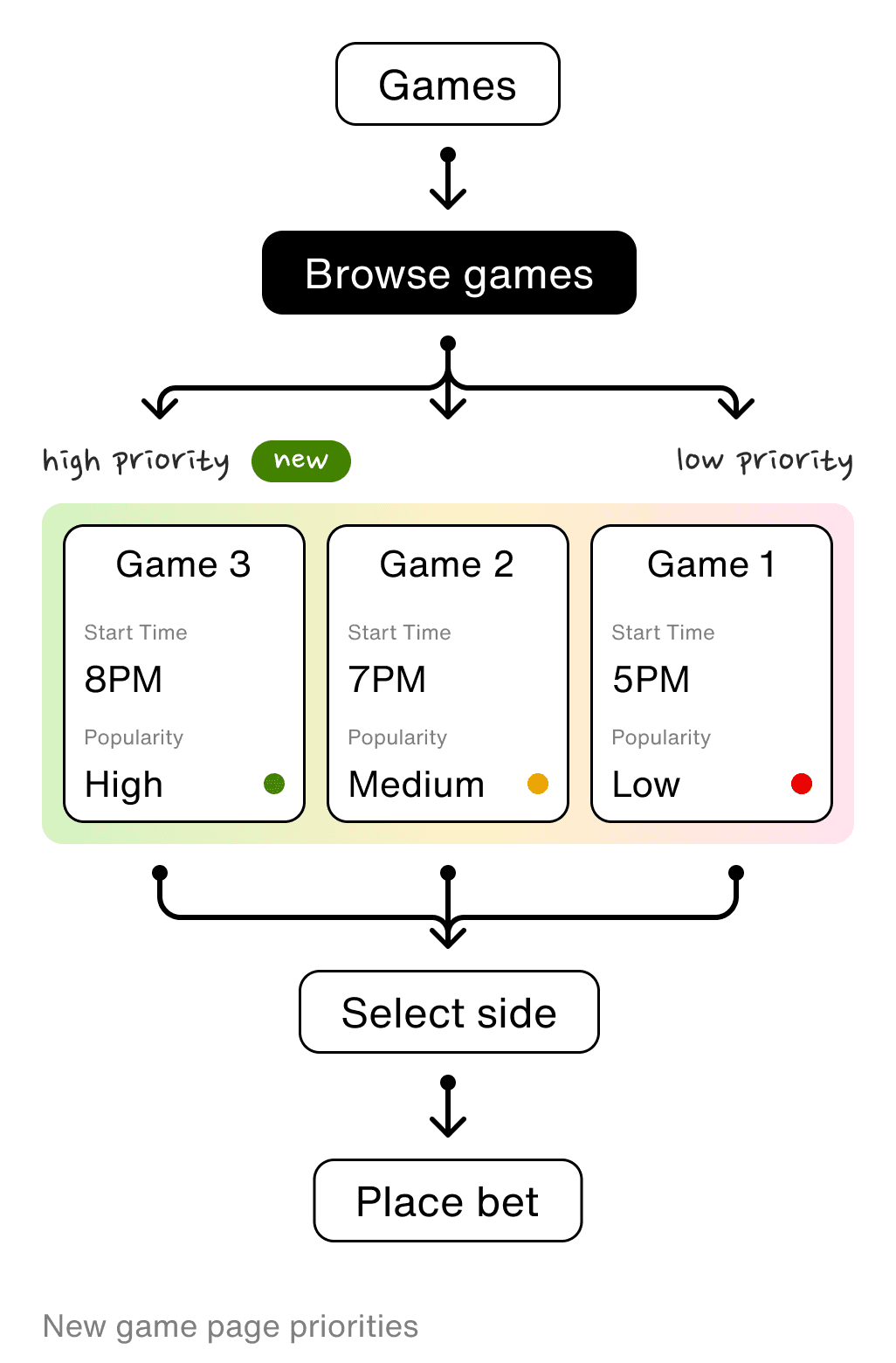
Originally, Wagr would display games in order of time, but I noticed a tendency for bets to favor trending games. To spur betting activity, I introduced a 'popular games' feature, which amplified engagement on important encounters.
Originally, Wagr would display games in order of time, but I noticed a tendency for bets to favor trending games. To spur betting activity, I introduced a 'popular games' feature, which amplified engagement on important encounters.
Originally, Wagr would display games in order of time, but I noticed a tendency for bets to favor trending games. To spur betting activity, I introduced a 'popular games' feature, which amplified engagement on important encounters.



Be bold about the strategy
Be bold about the strategy
Be bold about the strategy
How might we share this new feature to users in the most straightforward manner?
I explored various ways in which users could engage with a new feature over time. I wanted bet matching’s initial release to be bold and clear. I wanted later iterations to be seamless and intuitive.
How might we share this new feature to users in the most straightforward manner?
I explored various ways in which users could engage with a new feature over time. I wanted bet matching’s initial release to be bold and clear. I wanted later iterations to be seamless and intuitive.
How might we share this new feature to users in the most straightforward manner?
I explored various ways in which users could engage with a new feature over time. I wanted bet matching’s initial release to be bold and clear. I wanted later iterations to be seamless and intuitive.
Phasing in and out a feature
Phasing in and out a feature
Phasing in and out a feature


Phase 1: Bold and upfront
Phase 1: Bold and upfront
Phase 1: Bold and upfront


Phase 2: Clear messaging
Phase 2: Clear messaging
Phase 2: Clear messaging


Phase 3: Subtle reminders
Phase 3: Subtle reminders
Phase 3: Subtle reminders


Phase 4: Fully integrated
Phase 4: Fully integrated
Phase 4: Fully integrated
Take control of the narrative
Take control of the narrative
Take control of the narrative
How can I most effectively engage users in bet matching?
How can I most effectively engage users in bet matching?
How can I most effectively engage users in bet matching?
Identifying critical entry points for where users would consider bet matching the most.
Identifying critical entry points for where users would consider bet matching the most.
Identifying critical entry points for where users would consider bet matching the most.
What difference was made?
What difference was made?
What difference was made?
Matched bets
Matched bets
80%
80%
80%
+ 30%
+ 30%
Users saw an uptick in their number of bets being accepted
Users saw an uptick in their number of bets being accepted



